Crustaceans Workflow - Functional biogeography of invaders: the case of two widely distributed omnivorous crustaceans
Background<div>Biological invasions are acknowledged to be significant environmental and economic threats, yet the identification of key ecological traits determining invasiveness of species has remained elusive. One unappreciated source of variation concerns dietary flexibility of non-native species and their ability to shift trophic position within invaded food webs. Trophic plasticity may greatly influence invasion success as it facilitates colonisation, adaptation, and successful establishment of non-native species into new territories. In addition, having a flexible diet gives the introduced species a better chance to become invasive and, as a consequence, to have a strong impact on food webs, determining secondary disruptions such as trophic cascades and changes in energy fluxes. The deleterious effects can affect multiple trophic levels.</div><div><br></div><div>Introduction</div><div>Crustaceans are considered the most successful taxonomic group of aquatic invaders worldwide. Their ability to colonise and easily adapt to new ecosystems can be ascribed to a number of ecological features including their omnivorous feeding behaviour. This validation case study focuses on two invasive crustaceans widely distributed in marine and freshwater European waters: the Atlantic blue crab Callinectes sapidus and the Louisiana crayfish or red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii.
Callinectes sapidus and Procambarus clarkii are opportunistic omnivores that feed on a variety of food sources from detritus to plants and invertebrates. For this reason, they represent a good model to investigate the variation of trophic niches in invaded food webs and their ecological impact on native communities. The ecological consequences of the invasion and establishment of these invasive crustaceans can vary from modification of carbon cycles in benthic food webs to regulation of prey/predator abundance through bottom-up and top-down interactions. Understanding how the trophic ecology of these invasive crustaceans shapes benthic food webs in invaded ecosystems is crucial for an accurate assessment of their impact. The analysis of stable isotopes can provide important clues on the trophic effects of invasive species within non-native ecosystems by evaluating changes in their trophic position and characteristics of their trophic niche.</div><div><br></div><div>Aims</div><div>This validation case uses a collection of stable isotopes (δ13C and δ15N) of C. sapidus and P. clarkii and their potential prey in invaded food webs to quantify changes in the trophic position of the invaders and to assess post-invasion shifts in their dietary habits. This case study additionally evaluates the main environmental drivers involved in trophic niche adaptations and whether such bioclimatic predictors influence broad-scale patterns of variation in the trophic position of the invader.</div>
Default
- Date ( Publication)
- 2021-02-25
- Date ( Creation)
- 2019-07-04
- Status
- Under development / Pre operational
- Keywords
-
Crustaceans
- Keywords
-
IJI
- Access constraints
- License
- Use limitation
-
The final license will be available soon.
- OnLine resource
-
Info page
(
WWW:LINK-1.0-http--link
)
- OnLine resource
-
Run the workflow
(
WWW:LINK-1.0-http--link
)
- Service Name
-
Crustaceans WoRMS Taxonomic Checker
- Service Description
-
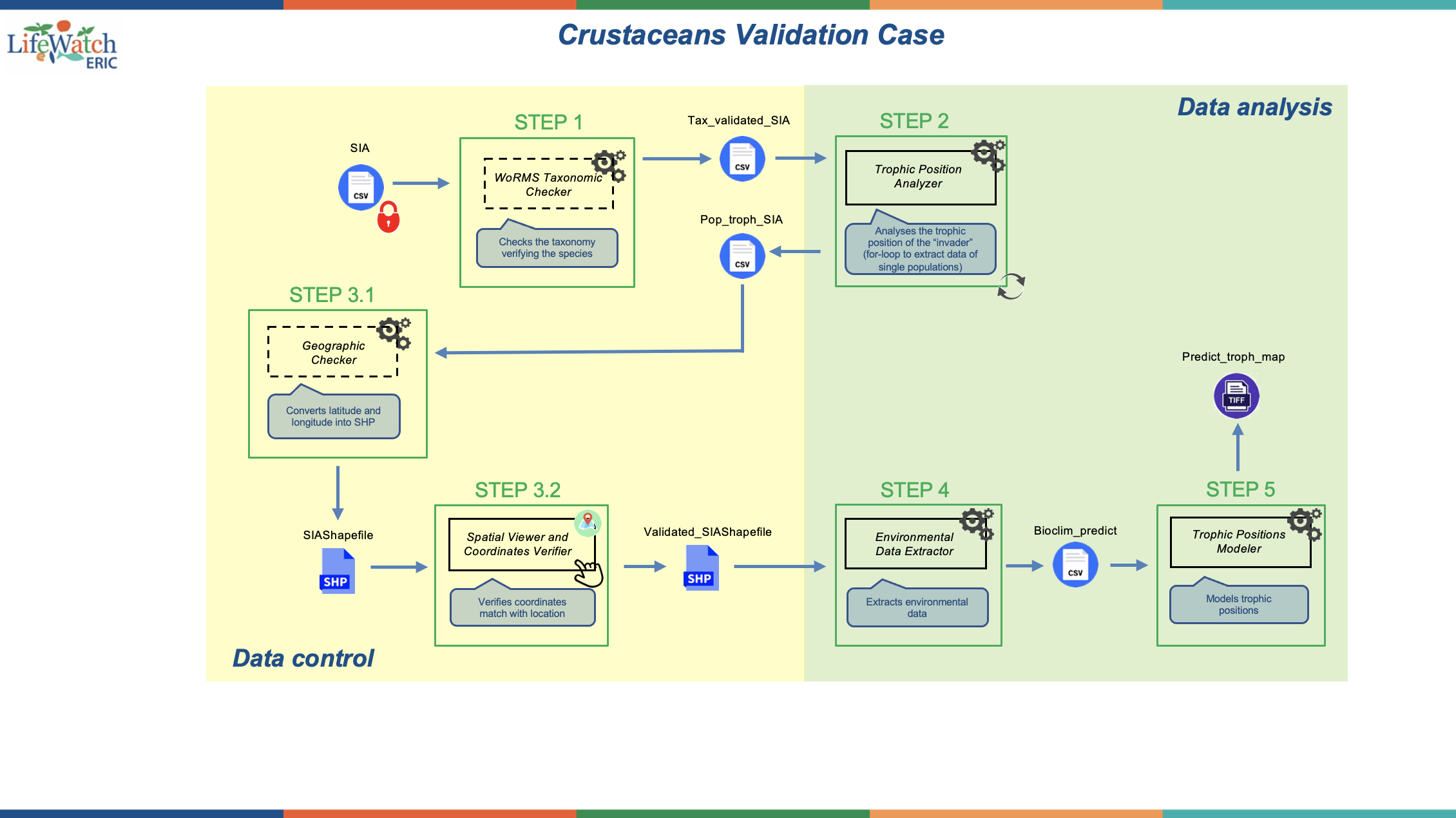
A service that aims at verifying the species names (performing the taxonomy check) by using the input file SIA.csv. It represents the Step 1.
- Service Reference (id)
- Service Name
-
Trophic Position Analyzer
- Service Description
-
A service that aims at analyzing the trophic position of the “invader” by using a Bayesian model to estimate the NA values of the trophic position that corresponds to the column 13 “TP” of the ""Tax_validated_SIA.csv” file by means of a loop that allows extracting data of single populations.
It represents the Step 2.
- Service Reference (id)
- Service Name
-
Geographic Checker
- Service Description
-
This service aims at creating a vector from the coordinates in the “Pop_troph_SIA.csv” file and convert it into a shapefile.
It represents the Step 3.1,
- Service Reference (id)
- Service Name
-
Spatial Viewer and Coordinates Verifier
- Service Description
-
A service that aims at verifying the coordinates (latitude and longitude in column 3 and 4 of file “Pop_trop_SIA.csv”) match with the location (“country” and “location” in column 1 and 2 of file “Pop_troph_SIA.csv”) using the “SIAShapefile.shp”. This is very important because these geographic coordinates will be used in other services to extract and retrieve environmental data on the location of the species observation/occurrence. So scientists need to ensure these coordinates are correct.
It represents the Step 3.2.
- Service Reference (id)
- Service Name
-
Environmental Data Extractor
- Service Description
-
This service aims to create a dataset of environmental predictors linked to SIA’s coordinates by exploiting oceanographic and bioclimatic raster layers. It extracts Enviromental Data and represents the Step 4.
- Service Reference (id)
- Service Name
-
Trophic Positions Modeler
- Service Description
-
This service aims at modeling trophic positions as a function of environmental drivers (e.g., through GAMs, etc.) by using the "Bioclim_predic.csv" file.
It represents the Step 5.
- Service Reference (id)
- Workflow Helpdesk
- Workflow Training
-
https://training.lifewatch.eu/resources/?resource=/course/view.php?id=37
Metadata
- File identifier
- 8f0a4b44-1858-45bb-a8f1-cea7d9baf6d4 XML
- Metadata language
- en
- Hierarchy level
- Workflow
- Metadata Schema Version
-
1.0
 Metadata Catalogue
Metadata Catalogue